The three core dimensions of Lean Agile Leadership are pivotal in transforming how organizations lead and deliver value.
Leaders in today’s fast-paced world face the challenge of guiding their teams effectively amidst rapidly changing environments.
The key dimensions of this leadership are Leading by Example, Mindset and Principles, and Leading Change, which serve as the foundation of effective Lean Agile practices.
By understanding and embracing these dimensions, leaders can better support their teams and foster a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability.
Lean Agile Leadership begins with adopting the right mindset and principles, which are crucial in aligning leaders with their organizations’ core values.
Embracing this mindset helps leaders create sustainable workflows and drive the organization toward its goals.
The approach encourages leaders to embody the principles they wish to instill in their teams, reinforcing a culture of trust and collaboration.
Applying these dimensions also involves actively leading change within an organization.
Leaders are tasked with inspiring their teams and driving transformative practices that lead to improved performance and innovation.
Mindset and Principles form one of the essential pillars, enabling leaders to champion change effectively.
As leaders embrace these principles, they lay the groundwork for successful Lean Agile transformations.
Understanding Lean Agile Leadership

Lean Agile Leadership is a critical responsibility in an organization’s transformation journey.
It focuses on guiding teams through Lean and Agile methodologies to achieve continuous improvement and greater efficiency while aligning with the company’s overall vision and values.
What is the Lean Agile Leadership?
Lean Agile Leadership blends the concepts of Lean thinking and Agile methodologies. It prioritizes value creation through efficient workflows, emphasizing the importance of a clear vision and consistent principles.
The three dimensions of lean agile leadership—leading by Example, Mindset and Principles, and Leading Change—play crucial roles in fostering an environment where agile practices can thrive.
In this setup, leadership is a core competency that enables the organization to work towards common goals and adapt efficiently to customer needs.
Importance in Today’s Business Environment
In today’s fast-paced business environment, Lean Agile Leadership is significant. It equips organizations to handle the complexities of modern business landscapes, ensuring they respond swiftly to new opportunities and customer demands.
Leadership in this context focuses on enhancing organizational agility and operational excellence.
For large organizations, Lean Agile Leadership helps scale agile practices, enabling the successful coordination of large numbers of agile teams and agile release trains.
This ensures that the organization remains competitive and can deliver customer value effectively through continuous flow and iterative development.
Key Principles of Lean Agile Leadership
Key principles of Lean Agile Leadership revolve around fostering a culture of continuous improvement and learning.
You are expected to embody these principles and set examples for team members by demonstrating servant leadership and emotional intelligence.
This approach encourages innovation and empowers cross-functional teams to achieve the highest potential.
Additionally, Lean Agile Leadership emphasizes the significance of the agile framework’s scale, which supports the alignment of team efforts across the enterprise.
It also promotes agile transformation across all levels, ensuring that small teams and major business units operate within an agile methodology framework. It aims to achieve the shortest sustainable lead time and improve project management outcomes.
The Three Core Dimensions of Lean Agile Leadership
The core dimensions of Lean Agile Leadership are crucial for driving effective organizational change and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
They guide leaders in navigating complexities and achieving greater efficiency in today’s dynamic business environment.
Dimension 1: Organizational Agility
Organizational agility involves adapting structures and processes to enhance flexibility and responsiveness.
In large organizations, achieving this requires shifting from traditional hierarchies to more fluid and cross-functional teams. Agile release trains integrate different teams to align their efforts toward common goals.
This dimension emphasizes the importance of a culture that values rapid decision-making and encourages team members to experiment without fear of failure.
Lean portfolio management plays a crucial role in aligning resources with strategic priorities.
This ensures that the entire organization is focused on delivering customer value efficiently.
The ability to pivot quickly in response to market changes creates a competitive advantage by satisfying and anticipating customer needs.
Dimension 2: Lean Thinking and Practices
Lean thinking involves optimizing processes to enhance efficiency and eliminate waste.
This dimension focuses on value streams that ensure every step in the development process adds value to the end product.
By employing set-based design and iterative development, teams can explore multiple design options and choose the most effective one.
Lean practices encourage continuous workflow, minimizing delays and maximizing productivity.
The principles underpinning lean thinking include respect for people, relentless improvement, and delivering the highest potential value.
Operational excellence is achieved by applying these principles, ensuring that processes are continuously refined.
Lean practices are essential for maintaining technical agility. They enable teams to innovate swiftly and deliver high-quality solutions in a digitally enabled business environment.
Dimension 3: Agile Methodologies
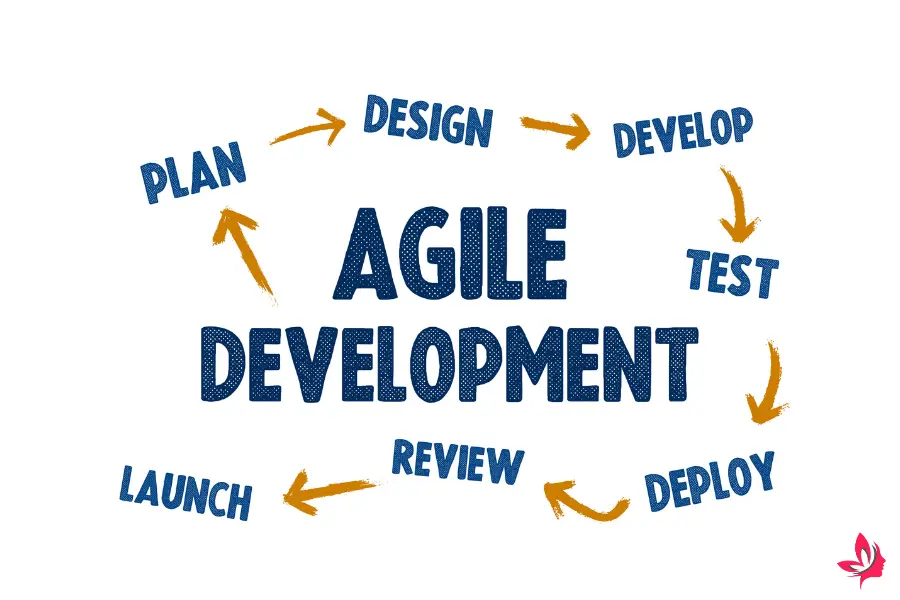
Agile methodologies focus on flexibility and iterative development. They are designed to empower teams to deliver in short cycles, enhancing adaptability.
Scrum masters and product owners facilitate these methodologies by ensuring teams remain focused on clear goals and customer feedback.
Implementing agile methodologies involves fostering a continuous learning culture within teams.
This encourages the ongoing improvement of lean-agile development practices.
Agile methodologies are a fundamental element of the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), designed to support large numbers of agile teams working cohesively.
Team leaders are critical in nurturing high-performing agile teams by removing obstacles and enabling a culture of collaboration.
Agile methods emphasize short feedback loops and the iterative testing of ideas to ensure solutions align with customer needs.
This iterative process helps organizations maintain a competitive edge by delivering tailored solutions promptly.
Embracing agile methodologies equips organizations to thrive in the complexities of modern business landscapes.
Building High-Performing Agile Teams

High-performing agile teams are essential for achieving efficiency and responsiveness in today’s dynamic business environment.
These teams understand core values such as transparency, adaptability, and continuous improvement to enhance performance and drive success.
Characteristics of High-Performing Teams
High-performing agile teams exhibit several key characteristics. They often are cross-functional, meaning team members possess diverse skills that complement one another.
This diversity is crucial for tackling complex problems and delivering innovative solutions in agile software development.
Communication is another cornerstone. Regular interactions ensure everyone stays aligned with a common goal, fostering a sense of trust and openness.
Consistent review of performance metrics helps them maintain their focus on customer satisfaction and value delivery, ensuring they meet the organization’s needs.
The Role of Team Members in Agile Success
Team members play a crucial role in Agile success by actively participating in Agile practices such as daily stand-ups, retrospectives, and sprint planning.
These practices help maintain a culture of continuous improvement, allowing for swift adaptation to changing requirements.
Efficient team members understand the importance of collaboration and take ownership of their work.
This responsibility extends to roles like the scrum master and product owner, which are vital in facilitating communication and removing obstacles.
Their proactive engagement leads to better decision-making and enhances the team’s ability to deliver on promises.
Continuous Learning Culture and Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is a critical component of high-performing agile teams. It allows team members to manage emotions effectively, improving collaboration and conflict resolution.
Leaders with emotional intelligence excel in supporting their teams through changes and challenges.
A continuous learning culture is essential for adapting to the digital age.
Training and workshops help team members stay updated on the latest tools and methodologies, fostering an environment where learning is prioritized.
Encouraging experimentation and reflecting on past performances cultivates an atmosphere where teams strive to exceed their highest potential.

Navigating organizational change within large organizations involves understanding the complexities of transition and actively addressing resistance. Effective leadership plays a crucial role by asking key questions and guiding the transformation journey.
The Transformation Journey in Large Organizations
In large organizations, transformation requires a clear vision and strategic planning that aligns with the organization’s goals.
Understanding the core dimensions of Lean Agile Leadership, which include mindset, values, and principles, is a crucial part of this process.
Agile transformation involves implementing frameworks like the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) to handle the challenges of modern business landscapes.
By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can achieve greater efficiency and responsiveness to customer needs.
Change management strategies should incorporate Agile practices and principles, enabling teams to alter workflows without disrupting ongoing projects.
Emphasizing the importance of team members’ roles ensures everyone is aligned with the transformation goals.
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Resistance is a natural part of organizational change, often arising from uncertainties and fear of the unknown.
Effective leaders can overcome this by promoting open communication and actively involving team members in the change process.
A culture of continuous learning helps reduce resistance, as it encourages team members to be adaptable and embrace new methodologies.
To gain widespread support, leaders should highlight the benefits of change, such as improved operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
Emotional intelligence plays a significant role in addressing concerns.
Leaders can foster trust and collaboration by acknowledging the personal and professional impacts of change.
Implementing iterative development allows teams to adjust and improve processes incrementally, reducing resistance.
Key Questions for Effective Leadership During Change
Leaders must ask key questions when steering organizational change to ensure alignment and progress.
Questions such as “How does this change align with our core values and mission?” and “What are the clear goals and objectives for this transformation?” help maintain focus.
Leaders should also consider the resources and capabilities needed to complete the transformation journey.
Understanding these core competencies is essential for managing the complexities of the transition phase.
To support effective change implementation, asking, “How will we measure success?” ensures that the organization remains accountable and transparent.
By identifying key performance indicators, leaders can monitor progress and make informed decisions to guide the transformation effectively.
Measuring Success in Lean Agile Leadership

Effective Lean Agile Leadership fosters agile principles and ensures continuous organizational improvement. Clear metrics are vital to evaluate how leadership strategies translate into organizational success.
Key Performance Indicators for Agile Organizations
Key performance indicators (KPIs) help gauge the effectiveness of agile practices and the dimensions of lean-agile leadership.
Metrics like velocity, lead time, and cycle time reveal the efficiency of agile methodologies.
Tracking velocity aids in measuring team productivity and progress.
Lead time, the duration between task initiation and completion, offers insights into the efficiency of the agile release trains.
Cycle time reflects the time taken to complete a task from start to finish, indicating the agile team’s operational excellence.
Together, these KPIs provide a robust framework for assessing lean-agile performance.
Assessing Customer Satisfaction and Value Delivery
Customer satisfaction is paramount in agile organizations. Evaluating this can identify areas where leadership must enhance product offerings.
Feedback loops, powered by agile practices, provide valuable insights into customer value.
Surveys and net promoter score (NPS) are effective tools for measuring customer satisfaction. They gauge how leadership strategies impact customer perception, helping refine core values and agile product delivery.
Success is often reflected in the continuous alignment of the development process with customer needs. This ensures that agile methodologies result in high customer value.
Continuous Improvement and Operational Excellence
Continuous improvement is integral to Lean Agile Leadership. This commitment to ongoing enhancement of organizational agility drives long-term success.
Lean thinking and iterative development nurture a culture of growth, encouraging agile transformation across the entire organization.
Implementing regular retrospectives allows teams to identify weaknesses and leverage new opportunities for enhancement.
Pursuing operational excellence requires lean portfolio management to optimize resources effectively and enhance technical agility.
Agile teams must maintain a clear vision, guided by transformative leadership, to achieve the organization’s highest potential through a continuous flow of innovative solutions.
Final Thoughts
Lean Agile Leadership emphasizes critical dimensions that guide successful teams. These dimensions include Mindset and Principles, SAFe Core Values, and Leading the Change. Each plays a crucial role in fostering an adaptive and efficient organization.
By embedding these aspects in leadership, organizations can better navigate challenges and support high-performing teams.
Adopting a Lean Agile mindset encourages continuous improvement and value creation. Leaders align decisions and actions with core values, promoting transparency and collaboration.
Moreover, they lead by example, inspiring teams to embrace change and innovate.
Fostering a strong mindset creates an environment where everyone is motivated to achieve sustainable workflows. This is vital for long-term success.
Strong leadership also requires understanding team dynamics and being flexible in approaches.
Key Takeaways:
- Mindset and Principles guide decision-making and innovation.
- SAFe Core Values ensure teams work towards common goals.
- Leading the Change requires active participation and support from all levels of the organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
Lean-Agile Leadership revolves around key principles that guide leaders in efficiently managing Agile processes. It includes dimensions that expand leadership qualities and strategies to improve team collaboration and project delivery.
What are the three dimensions of Lean Agile Leadership?
The three dimensions of Lean Agile Leadership typically include Mindset and Principles, SAFe Core Values, and Leading Change. These elements guide leaders in creating value and effectively embracing change.
What are the 3 C’s of Agile Leadership?
The 3 C’s of Agile Leadership refer to Clarity, Commitment, and Communication. Leaders harness these attributes to facilitate team collaboration and ensure the alignment of goals and execution.
What are the three traits of an agile leader?
Agile leaders often embody adaptability, visionary thinking, and empowerment. These traits help them navigate changing environments and inspire their teams to achieve strategic goals.
What is the leading by example dimension of Lean Agile Leadership?
Leading by Example involves demonstrating behaviors and actions that reflect Agile values and principles. This dimension underscores the importance of role modeling in influencing team culture and attitudes toward change.
What are the three dimensions of leadership?
Leadership generally includes dimensions like Strategy, Execution, and Culture. These elements are crucial for driving organizational success and fostering an environment conducive to innovation and collaboration.
What are the three main elements of Agile?
The main elements of Agile include Iterative Development, Customer Collaboration, and Flexible Response to Change. These are fundamental to achieving project goals efficiently and with a focus on customer satisfaction.
What are the three pillars of Agile?
The three pillars of Agile are Transparency, Inspection, and Adaptation. These principles support continuous improvement and help align project developments with business objectives.
What are the three perspectives of Lean?
Lean perspectives can be categorized into Value Stream Mapping, Continuous Improvement, and Waste Reduction. These focus on enhancing efficiency and eliminating any processes that do not add value.
What are the dimensions of Agile?
Agile dimensions typically span Collaboration, Flexibility, and Responsiveness. These aspects help teams adapt quickly to changes and maintain an adequate workflow throughout the project lifecycle.
What is one of the dimensions of Lean Agile Leadership brainly?
One dimension of Lean-Agile Leadership is Leading by Example. This dimension emphasizes the importance of actions in reinforcing Agile principles and creating a culture of accountability and growth.